Secret Mathematical Rule Discovered to Shape Bird Beaks for 200 Million Years
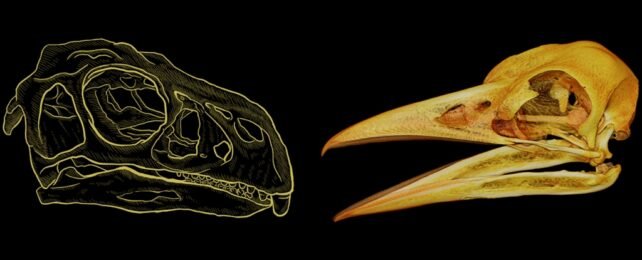
New research has uncovered a hidden mathematical rule that has been shaping the diverse forms of bird beaks for over 200 million years. This rule, revealed in a recent study, provides critical insight into how the faces of birds and their dinosaur ancestors evolved through time.
Bird beaks come in a remarkable variety, from the slender, straw-like beak of a hummingbird to the powerful, slicing beak of an eagle. Despite this incredible diversity, scientists have found that a single, mathematical principle governs the growth and shape of beaks in nearly all living birds—and even in dinosaurs. This principle is known as the power cascade.
The power cascade rule describes how the width of a pointed structure—such as a beak—expands from its tip to the base. This simple but universal rule not only helps explain the beak forms seen in nature but also sheds light on the evolution of other pointed structures like teeth, horns, hooves, and shells.
The discovery of such a universal biological rule is rare, making this finding especially significant. By applying this mathematical framework to the fossil record, researchers are now able to better understand the evolutionary processes that created the incredible diversity of bird beaks seen today and throughout history. In rare cases where organisms deviate from this rule, scientists can also explore the evolutionary advantages or pressures that drove those exceptions.
Recent Science Articles
NASA's Lucy Probe Sends Striking Close-Ups of Peanut-Shaped Asteroid Donaldjohanson
NASA's Lucy mission captured its first detailed images of the peanut-shaped asteroid Donaldjohanson, revealing its unusual geology and complex structure …
Arctic Meltdown Threatens Carbon Sinks: New Study Reveals Climate Change Impact on Polar Ecosystems
New research reveals climate change is undermining Arctic fjords' ability to sequester carbon, with shifting phytoplankton communities and melting ice …
Groundbreaking Study Reveals Complex Dynamics of the Brain's Serotonin System
University of Ottawa research reveals serotonin neurons' complex interactions and role in future reward signaling, offering new therapeutic insights.
NISAR Mission Launch Confirmed: NASA-ISRO's Earth Observation Satellite Set for June 2025
The groundbreaking NASA-ISRO NISAR satellite, designed to monitor Earth's ecosystems with unprecedented precision, is confirmed to launch in June 2025 …
Kindness Redefines Happiness: World Happiness Report 2025 Reveals Surprising Trends
The World Happiness Report 2025 reveals that happiness stems from both personal kindness and strong social connections, with Nordic countries …

NASA's Lucy Probe Sends Striking Close-Ups of Peanut-Shaped Asteroid Donaldjohanson
NASA's Lucy mission captured its first detailed images of the peanut-shaped asteroid Donaldjohanson, revealing its …

Arctic Meltdown Threatens Carbon Sinks: New Study Reveals Climate Change Impact on Polar Ecosystems
New research reveals climate change is undermining Arctic fjords' ability to sequester carbon, with shifting …

Groundbreaking Study Reveals Complex Dynamics of the Brain's Serotonin System
University of Ottawa research reveals serotonin neurons' complex interactions and role in future reward signaling, …




